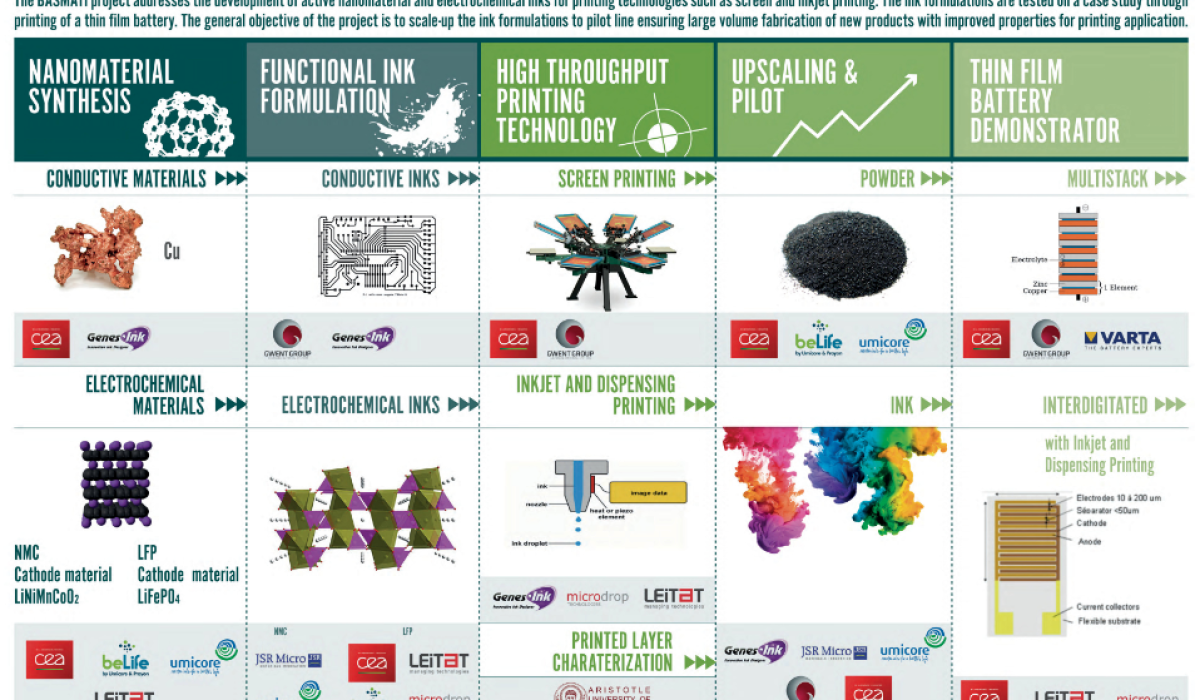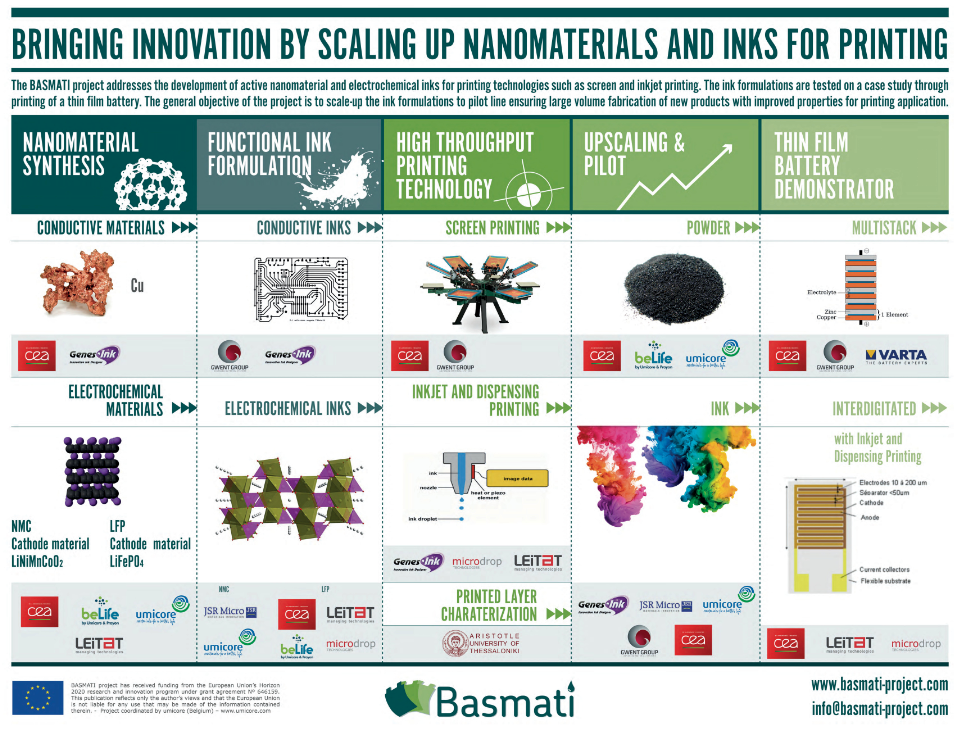
Bringing innovation by scaling up nanomaterials and inks for printing! This is the challenge of the BASMATI H2020 project. It addresses the development of active nanomaterial and electrochemical inks for printing technologies such as screen and inkjet printing. The ink formulations are tested on a case study through printing on a thin film battery. The general objective of the project is to scale-up the ink formulations to pilot line ensuring large volume fabrication of new product with improved properties for printing application.
Click here to download the poster!
BASMATI will also provide a new source of nanomaterials for the formulation of conductive and electrochemical inks. These nanomaterials will include metallic particles (Ni, Cu, Al) that will be usable for numerous applications of printed electronics on flexible substrates. Another type of nanomaterials will be layered positive active materials, such as LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 (NMC) and olivine LiFePO4 (LFP).
The know-how level reached in BASMATI by research groups, along with the transfer and up-scaling to pilots (TRL 6) at SMEs and industry facilities, will pave the way for the future industrialization of ink formulations for mass markets, such as printed electronics. The compatible formulations in high-throughput technologies will ensure a reproducible and reliable process for sophisticated, fully digital micro-structured devices. Nanosafety will also be carefully considered in the BASMATI project.